
单例
懒汉式: 方法上加synchronized
if (single == null) {
single = new Singleton();
}
return single;
}
懒汉式: 使用双检锁 + volatile
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (singleton == null) {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = new Singleton();
}
}
}
return singleton;
}
懒汉式: 使用静态内部类
private static class LazyHolder {
private static final Singleton INSTANCE = new Singleton();
}
private Singleton (){}
public static final Singleton getInstance() {
return LazyHolder.INSTANCE;
}
}
饿汉式
private Singleton1() {}
private static final Singleton1 single = new Singleton1();
public static Singleton1 getInstance() {
return single;
}
}
Future模式

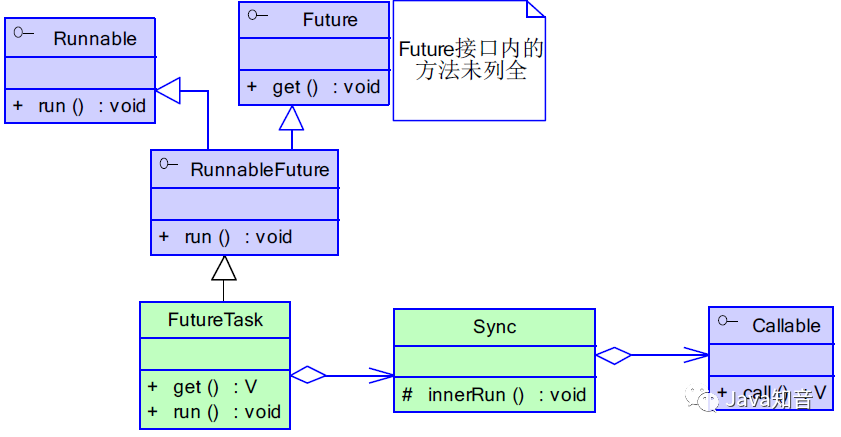
通过FutureTask实现
- 如果doOtherThing耗时2s, 则整个函数耗时2s左右.
- 如果doOtherThing耗时0.2s, 则整个函数耗时取决于RealData.costTime, 即1s左右结束.
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
FutureTask
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
return new RealData().costTime();
}
});
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
service.submit(future);
System.out.println(“RealData方法调用完毕”);
// 模拟主函数中其他耗时操作
doOtherThing();
// 获取RealData方法的结果
System.out.println(future.get());
}
private static void doOtherThing() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(2000L);
}
}
class RealData {
public String costTime() {
try {
// 模拟RealData耗时操作
Thread.sleep(1000L);
return “result”;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return “exception”;
}
}
通过Future实现
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Future
System.out.println(“RealData2方法调用完毕”);
// 模拟主函数中其他耗时操作
doOtherThing();
// 获取RealData2方法的结果
System.out.println(future.get());
}
private static void doOtherThing() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(2000L);
}
}
class RealData2 implements CallableString>{
public String costTime() {
try {
// 模拟RealData耗时操作
Thread.sleep(1000L);
return “result”;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return “exception”;
}
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
return costTime();
}
}
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
// 是否已经取消
boolean isCancelled();
// 是否已经完成
boolean isDone();
// 取得返回对象
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
// 取得返回对象, 并可以设置超时时间
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
生产消费者模式

生产者核心代码
Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(SLEEP_TIME));
data = new PCData(count.incrementAndGet);
// 构造任务数据
System.out.println(data + ” is put into queue”);
if (!queue.offer(data, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
// 将数据放入队列缓冲区中
System.out.println(“faild to put data : “ + data);
}
}
消费者核心代码
PCData data = queue.take();
// 提取任务
if (data != null) {
// 获取数据, 执行计算操作
int re = data.getData() * 10;
System.out.println(“after cal, value is : “ + re);
Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(SLEEP_TIME));
}
}
分而治之
Master-Worker模式
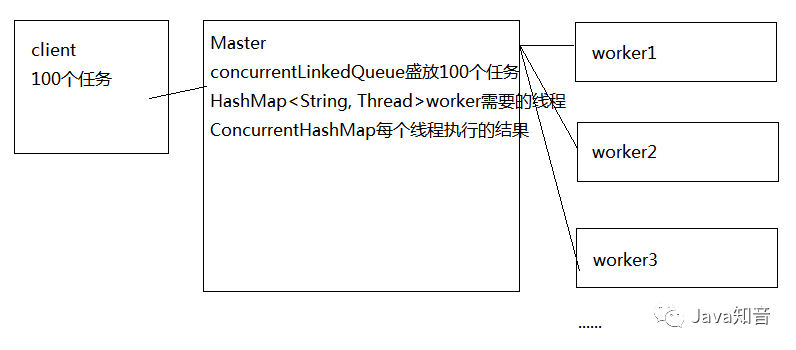
// 盛装任务的集合
private ConcurrentLinkedQueue
// 所有worker
private HashMap
// 每一个worker并行执行任务的结果
private ConcurrentHashMap
public MasterDemo(WorkerDemo worker, int workerCount) {
// 每个worker对象都需要持有queue的引用, 用于领任务与提交结果
worker.setResultMap(resultMap);
worker.setWorkQueue(workQueue);
for (int i = 0; i workers.put(“子节点: “ + i, new Thread(worker));
}
}
// 提交任务
public void submit(TaskDemo task) {
workQueue.add(task);
}
// 启动所有的子任务
public void execute(){
for (Map.Entry
entry.getValue().start();
}
}
// 判断所有的任务是否执行结束
public boolean isComplete() {
for (Map.Entry
if (entry.getValue().getState() != Thread.State.TERMINATED) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// 获取最终汇总的结果
public int getResult() {
int result = 0;
for (Map.Entry
result += Integer.parseInt(entry.getValue().toString());
}
return result;
}
}
private ConcurrentLinkedQueue
private ConcurrentHashMap
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
TaskDemo input = this.workQueue.poll();
// 所有任务已经执行完毕
if (input == null) {
break;
}
// 模拟对task进行处理, 返回结果
int result = input.getPrice();
this.resultMap.put(input.getId() + “”, result);
System.out.println(“任务执行完毕, 当前线程: “ + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
public ConcurrentLinkedQueue
return workQueue;
}
public void setWorkQueue(ConcurrentLinkedQueue
this.workQueue = workQueue;
}
public ConcurrentHashMap
return resultMap;
}
public void setResultMap(ConcurrentHashMap
this.resultMap = resultMap;
}
}
private int id;
private String name;
private int price;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i 100; i++) {
TaskDemo task = new TaskDemo();
task.setId(i);
task.setName(“任务” + i);
task.setPrice(new Random().nextInt(10000));
master.submit(task);
}
master.execute();
while (true) {
if (master.isComplete()) {
System.out.println(“执行的结果为: “ + master.getResult());
break;
}
}
ForkJoin线程池
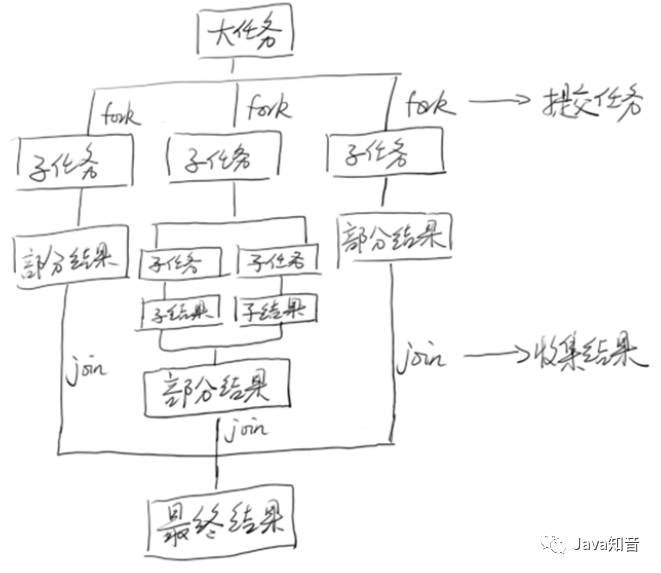
// 任务分解的阈值
private static final int THRESHOLD = 10000;
private long start;
private long end;
public CountTask(long start, long end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
public Long compute() {
long sum = 0;
boolean canCompute = (end – start) if (canCompute) {
for (long i = start; i sum += i;
}
} else {
// 分成100个小任务
long step = (start + end) / 100;
ArrayList
long pos = start;
for (int i = 0; i 100; i++) {
long lastOne = pos + step;
if (lastOne > end) {
lastOne = end;
}
CountTask subTask = new CountTask(pos, lastOne);
pos += step + 1;
// 将子任务推向线程池
subTasks.add(subTask);
subTask.fork();
}
for (CountTask task : subTasks) {
// 对结果进行join
sum += task.join();
}
}
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
// 累加求和 0 -> 20000000L
CountTask task = new CountTask(0, 20000000L);
ForkJoinTask
System.out.println(“sum result : “ + result.get());
}
}
0 条评论