一、Spring Web MVC 与 Spring Bean 注解
Spring Web MVC 注解
@RequestMapping
@RequestMapping注解的主要用途是将Web请求与请求处理类中的方法进行映射。Spring MVC和Spring WebFlux都通过RquestMappingHandlerMapping和RequestMappingHndlerAdapter两个类来提供对@RequestMapping注解的支持。
@RequestMapping注解对请求处理类中的请求处理方法进行标注;@RequestMapping注解拥有以下的六个配置属性:
-
value:映射的请求URL或者其别名 -
method:兼容HTTP的方法名 -
params:根据HTTP参数的存在、缺省或值对请求进行过滤 -
header:根据HTTP Header的存在、缺省或值对请求进行过滤 -
consume:设定在HTTP请求正文中允许使用的媒体类型 -
product:在HTTP响应体中允许使用的媒体类型
提示:在使用@RequestMapping之前,请求处理类还需要使用@Controller或@RestController进行标记
下面是使用@RequestMapping的两个示例:

@RequestMapping还可以对类进行标记,这样类中的处理方法在映射请求路径时,会自动将类上@RequestMapping设置的value拼接到方法中映射路径之前,如下:

@RequestBody
@RequestBody在处理请求方法的参数列表中使用,它可以将请求主体中的参数绑定到一个对象中,请求主体参数是通过HttpMessageConverter传递的,根据请求主体中的参数名与对象的属性名进行匹配并绑定值。此外,还可以通过@Valid注解对请求主体中的参数进行校验。
下面是一个使用@RequestBody的示例:

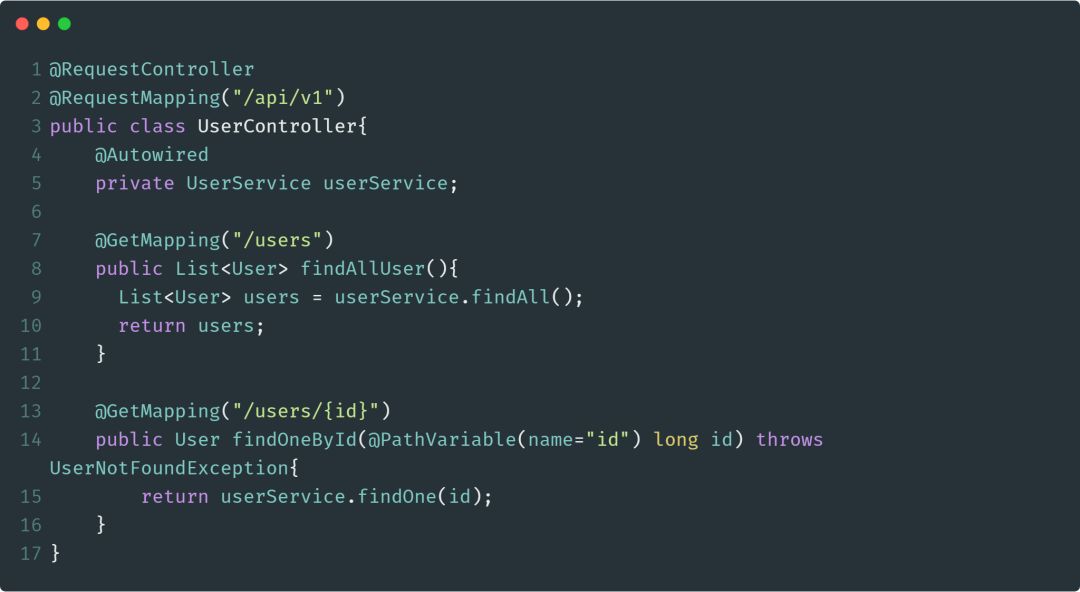
@GetMapping
@GetMapping注解用于处理HTTP GET请求,并将请求映射到具体的处理方法中。具体来说,@GetMapping是一个组合注解,它相当于是@RequestMapping(method=RequestMethod.GET)的快捷方式。
下面是@GetMapping的一个使用示例:
@PostMapping
@PostMapping注解用于处理HTTP POST请求,并将请求映射到具体的处理方法中。@PostMapping与@GetMapping一样,也是一个组合注解,它相当于是@RequestMapping(method=HttpMethod.POST)的快捷方式。
下面是使用@PostMapping的一个示例:

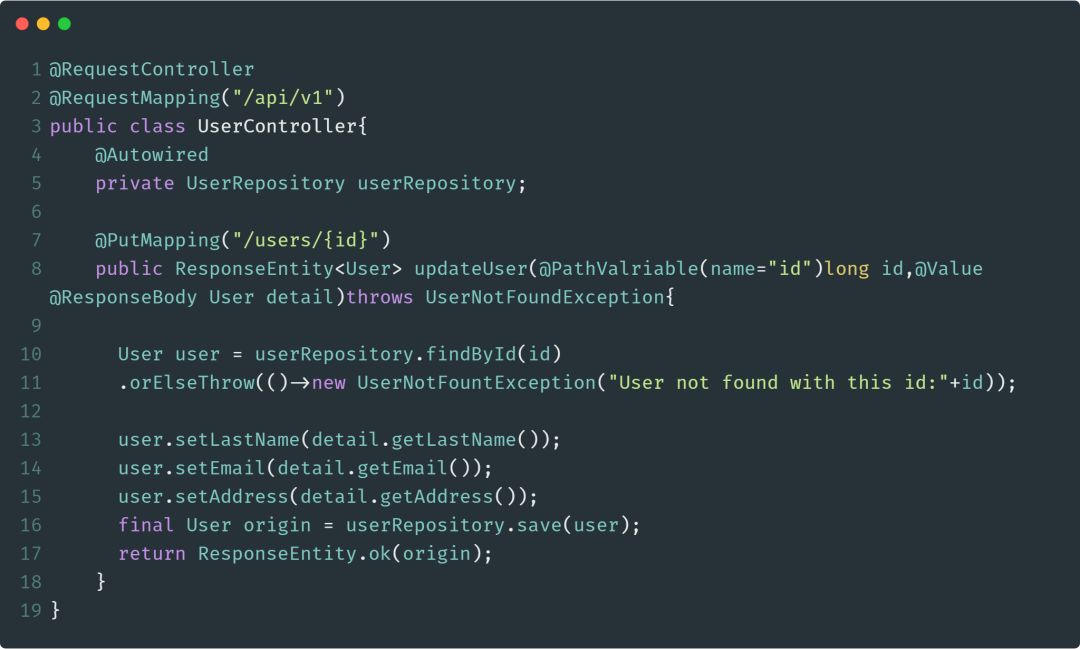
@PutMapping
@PutMapping注解用于处理HTTP PUT请求,并将请求映射到具体的处理方法中,@PutMapping是一个组合注解,相当于是@RequestMapping(method=HttpMethod.PUT)的快捷方式。
下面是使用@PutMapping的一个示例:
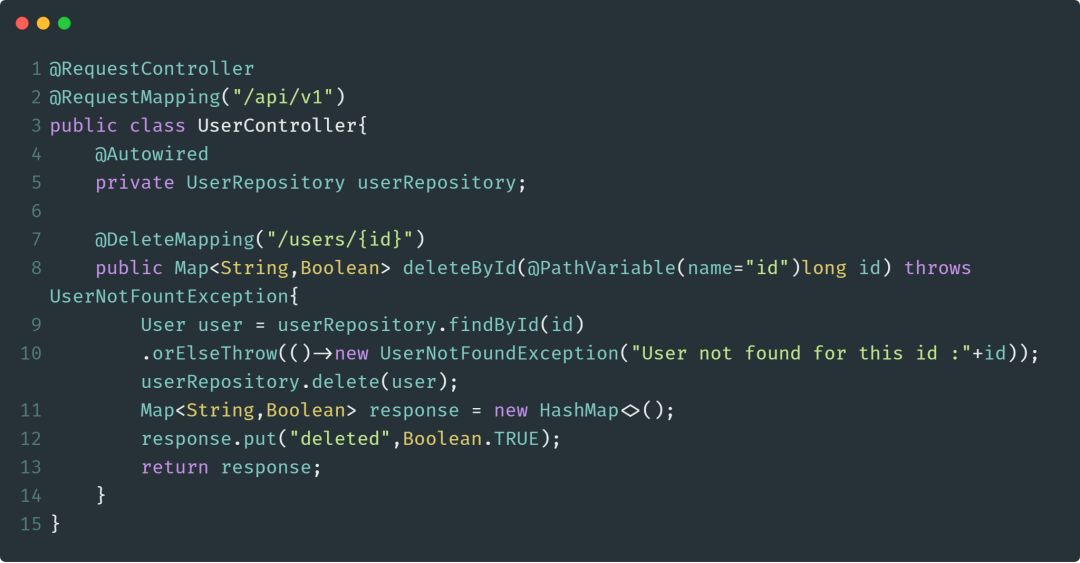
@DeleteMapping
@DeleteMapping注解用于处理HTTP DELETE请求,并将请求映射到删除方法中。@DeleteMapping是一个组合注解,它相当于是@RequestMapping(method=HttpMethod.DELETE)的快捷方式。
下面是使用@DeleteMapping的一个示例:
@PatchMapping
@PatchMapping注解用于处理HTTP PATCH请求,并将请求映射到对应的处理方法中。@PatchMapping相当于是@RequestMapping(method=HttpMethod.PATCH)的快捷方式。
下面是一个简单的示例:

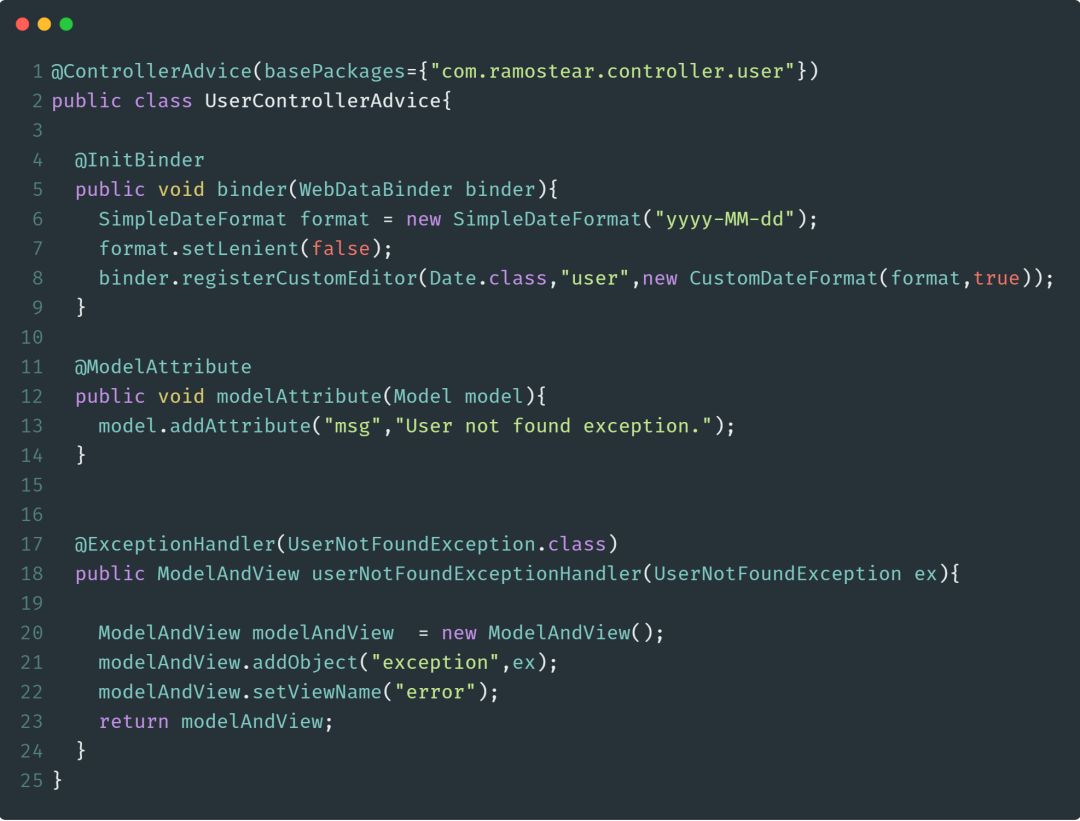
@ControllerAdvice
@ControllerAdvice是@Component注解的一个延伸注解,Spring会自动扫描并检测被@ControllerAdvice所标注的类。@ControllerAdvice需要和@ExceptionHandler、@InitBinder以及@ModelAttribute注解搭配使用,主要是用来处理控制器所抛出的异常信息。
首先,我们需要定义一个被@ControllerAdvice所标注的类,在该类中,定义一个用于处理具体异常的方法,并使用@ExceptionHandler注解进行标记。
此外,在有必要的时候,可以使用@InitBinder在类中进行全局的配置,还可以使用@ModelAttribute配置与视图相关的参数。使用@ControllerAdvice注解,就可以快速的创建统一的,自定义的异常处理类。
下面是一个使用@ControllerAdvice的示例代码:
@ResponseBody
@ResponseBody会自动将控制器中方法的返回值写入到HTTP响应中。特别的,@ResponseBody注解只能用在被@Controller注解标记的类中。如果在被@RestController标记的类中,则方法不需要使用@ResponseBody注解进行标注。@RestController相当于是@Controller和@ResponseBody的组合注解。
下面是使用该注解的一个示例

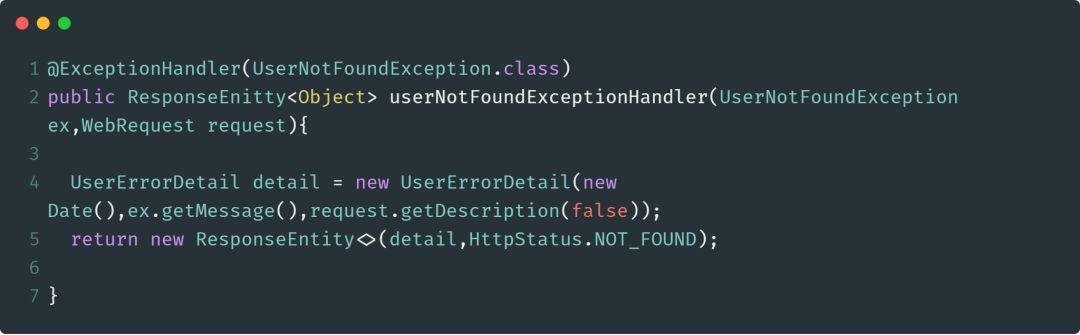
@ExceptionHandler
@ExceptionHander注解用于标注处理特定类型异常类所抛出异常的方法。当控制器中的方法抛出异常时,Spring会自动捕获异常,并将捕获的异常信息传递给被@ExceptionHandler标注的方法。
下面是使用该注解的一个示例:
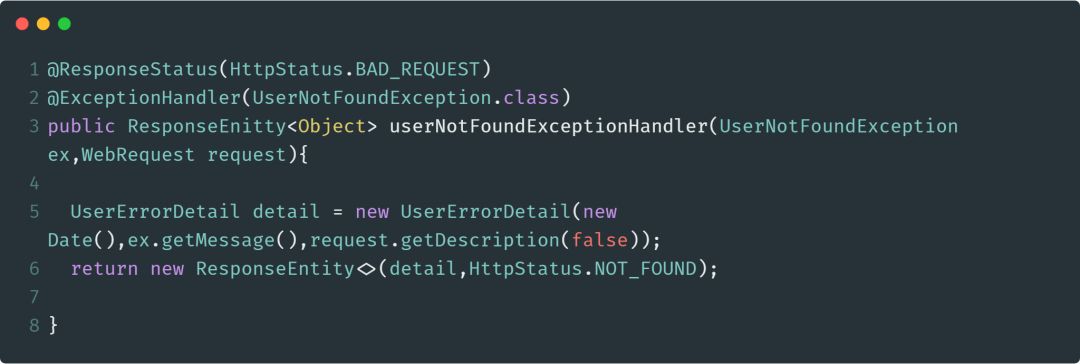
@ResponseStatus
@ResponseStatus注解可以标注请求处理方法。使用此注解,可以指定响应所需要的HTTP STATUS。特别地,我们可以使用HttpStauts类对该注解的value属性进行赋值。
下面是使用@ResponseStatus注解的一个示例:
@PathVariable
@PathVariable注解是将方法中的参数绑定到请求URI中的模板变量上。可以通过@RequestMapping注解来指定URI的模板变量,然后使用@PathVariable注解将方法中的参数绑定到模板变量上。
特别地,@PathVariable注解允许我们使用value或name属性来给参数取一个别名。下面是使用此注解的一个示例:

模板变量名需要使用{ }进行包裹,如果方法的参数名与URI模板变量名一致,则在@PathVariable中就可以省略别名的定义。
下面是一个简写的示例:

提示:如果参数是一个非必须的,可选的项,则可以在@PathVariable中设置require = false
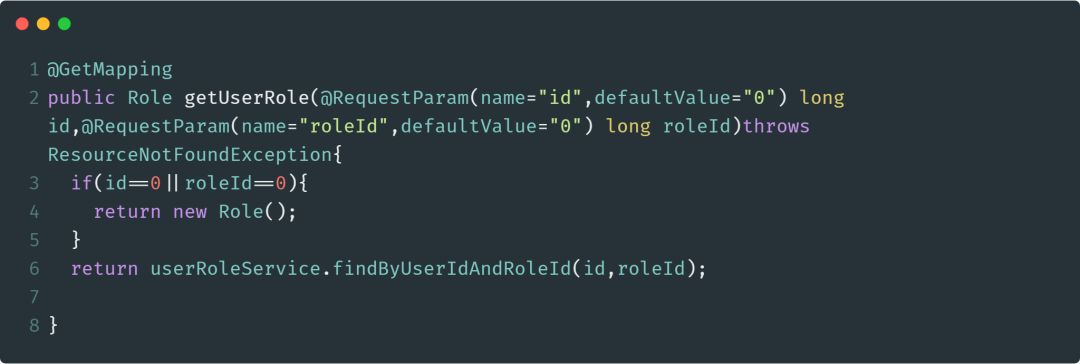
@RequestParam
@RequestParam注解用于将方法的参数与Web请求的传递的参数进行绑定。使用@RequestParam可以轻松的访问HTTP请求参数的值。
下面是使用该注解的代码示例:

该注解的其他属性配置与@PathVariable的配置相同,特别的,如果传递的参数为空,还可以通过defaultValue设置一个默认值。示例代码如下:
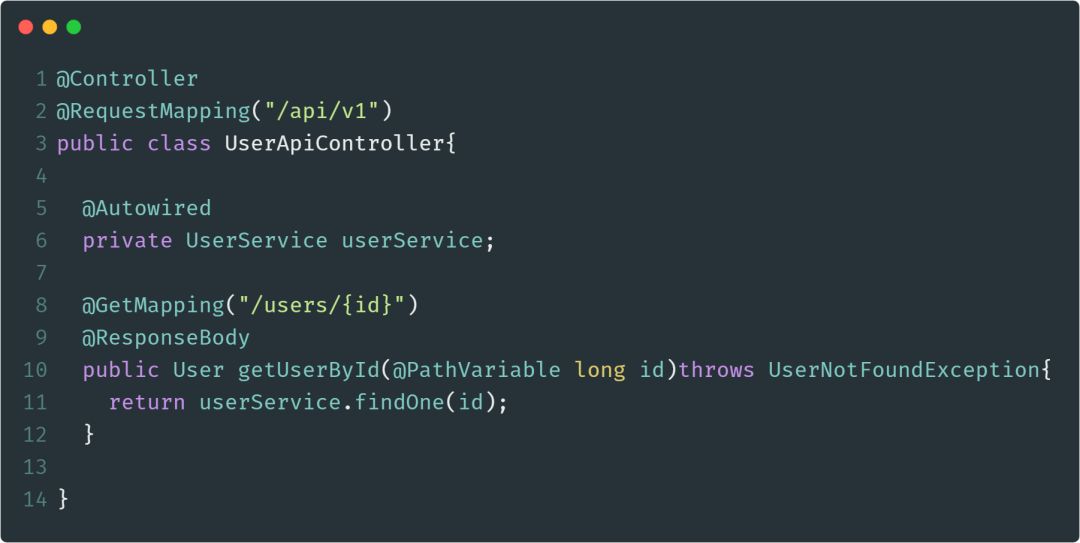
@Controller
@Controller是@Component注解的一个延伸,
会自动扫描并配置被该注解标注的类。此注解用于标注Spring MVC的控制器。下面是使用此注解的示例代码:
@RestController
@RestController是在Spring 4.0开始引入的,这是一个特定的控制器注解。此注解相当于@Controller和@ResponseBody的快捷方式。当使用此注解时,不需要再在方法上使用@ResponseBody注解。
下面是使用此注解的示例代码:

@ModelAttribute
通过此注解,可以通过模型索引名称来访问已经存在于控制器中的model。下面是使用此注解的一个简单示例:

与@PathVariable和@RequestParam注解一样,如果参数名与模型具有相同的名字,则不必指定索引名称,简写示例如下:

特别地,如果使用@ModelAttribute对方法进行标注,Spring会将方法的返回值绑定到具体的Model上。示例如下:
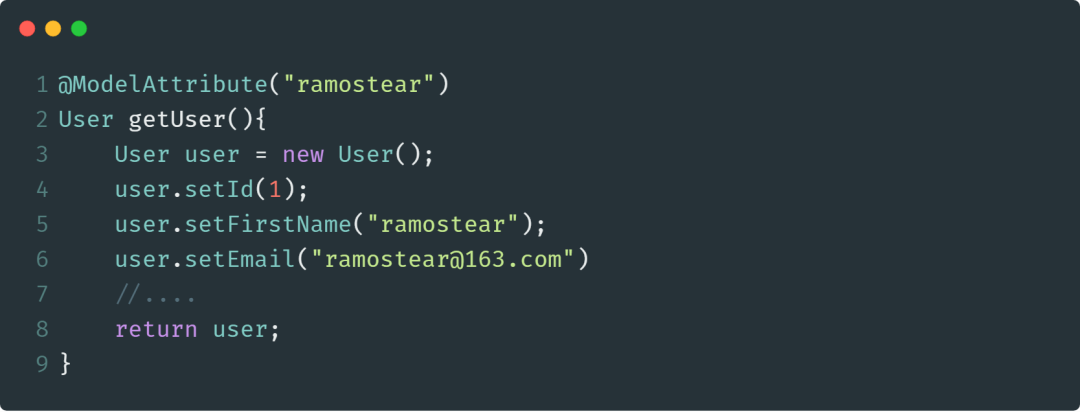
在Spring调用具体的处理方法之前,被@ModelAttribute注解标注的所有方法都将被执行。
@CrossOrigin
@CrossOrigin注解将为请求处理类或请求处理方法提供跨域调用支持。如果我们将此注解标注类,那么类中的所有方法都将获得支持跨域的能力。使用此注解的好处是可以微调跨域行为。使用此注解的示例如下:
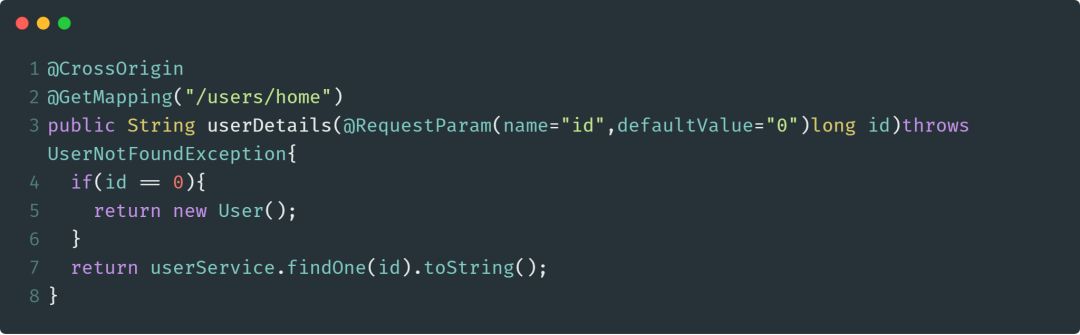
@InitBinder
@InitBinder注解用于标注初始化WebDataBinider的方法,该方法用于对Http请求传递的表单数据进行处理,如时间格式化、字符串处理等。下面是使用此注解的示例:

二、Spring Bean 注解
在本小节中,主要列举与Spring Bean相关的4个注解以及它们的使用方式。
@ComponentScan
@ComponentScan注解用于配置Spring需要扫描的被组件注解注释的类所在的包。可以通过配置其basePackages属性或者value属性来配置需要扫描的包路径。value属性是basePackages的别名。此注解的用法如下:
@Component
@Component注解用于标注一个普通的组件类,它没有明确的业务范围,只是通知Spring被此注解的类需要被纳入到Spring Bean容器中并进行管理。此注解的使用示例如下:
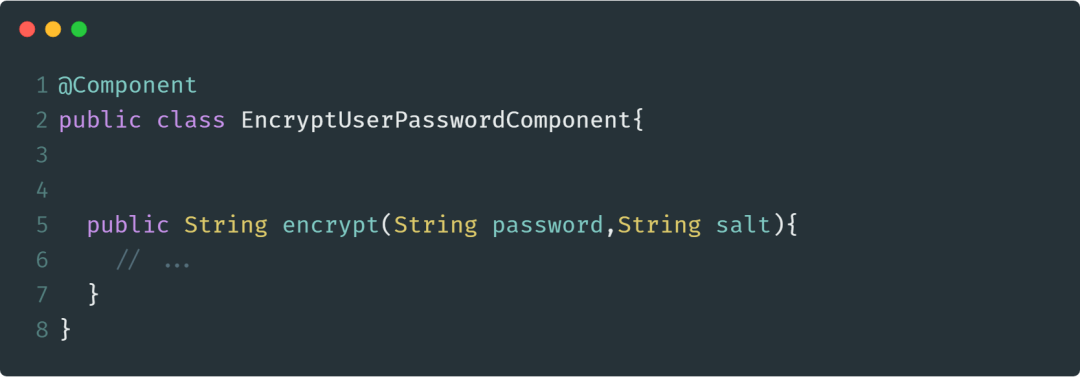
@Service
@Service注解是@Component的一个延伸(特例),它用于标注业务逻辑类。与@Component注解一样,被此注解标注的类,会自动被Spring所管理。下面是使用@Service注解的示例:
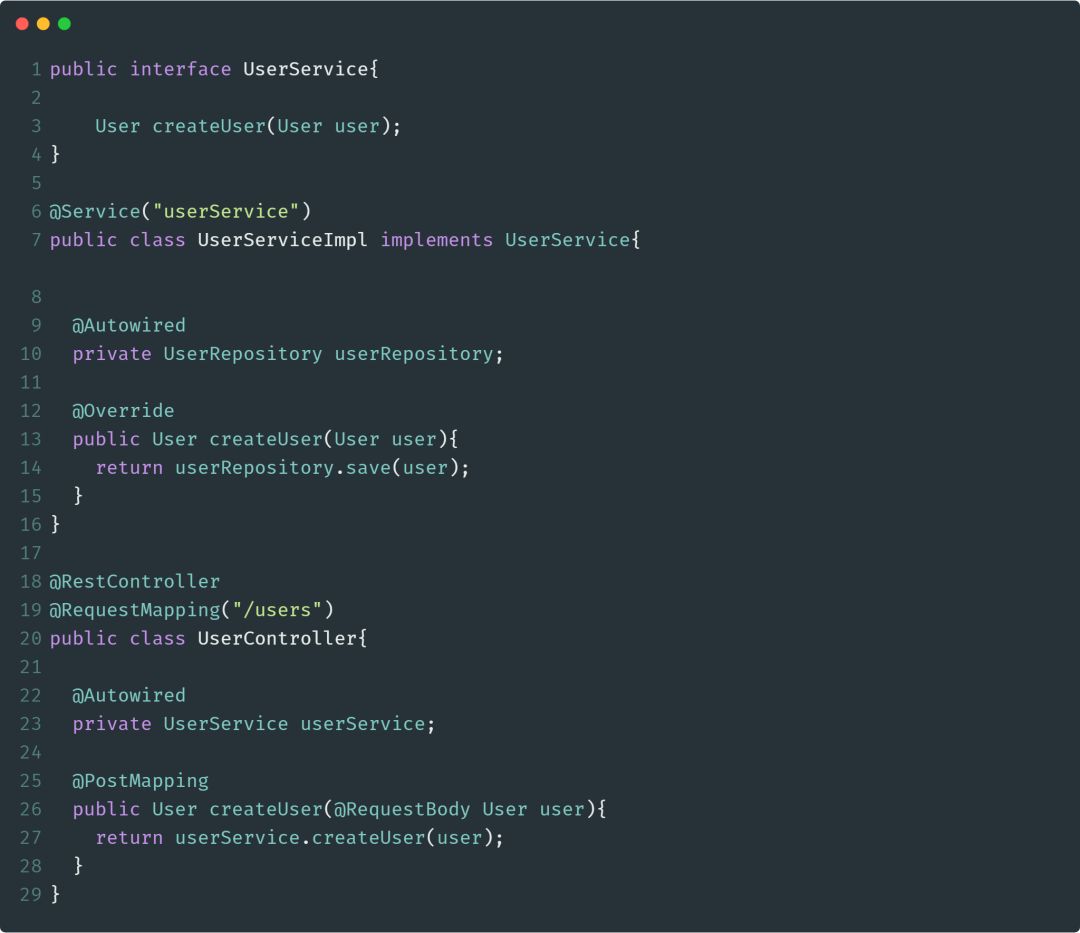
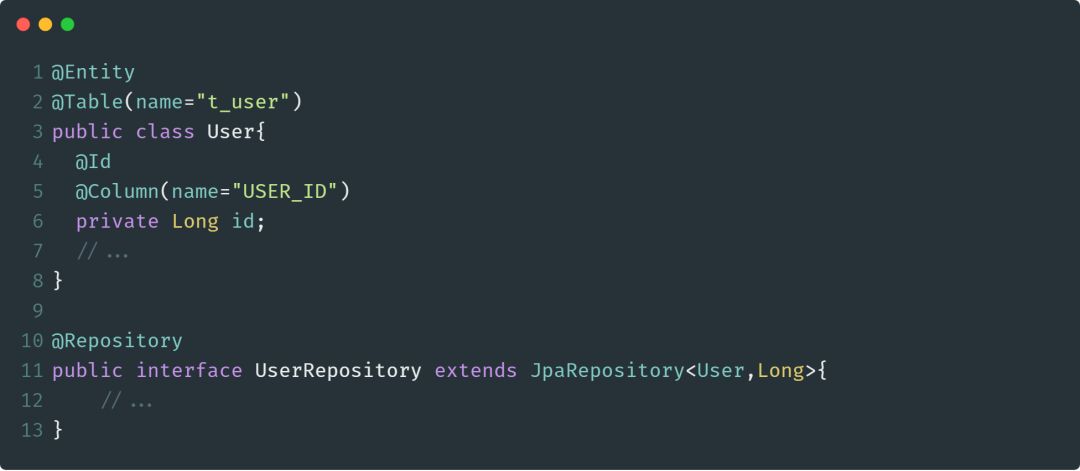
@Repository
@Repository注解也是@Component注解的延伸,与@Component注解一样,被此注解标注的类会被Spring自动管理起来,@Repository注解用于标注DAO层的数据持久化类。此注解的用法如下:
三、Spring Dependency Inject 与 Bean Scops注解
Spring DI注解
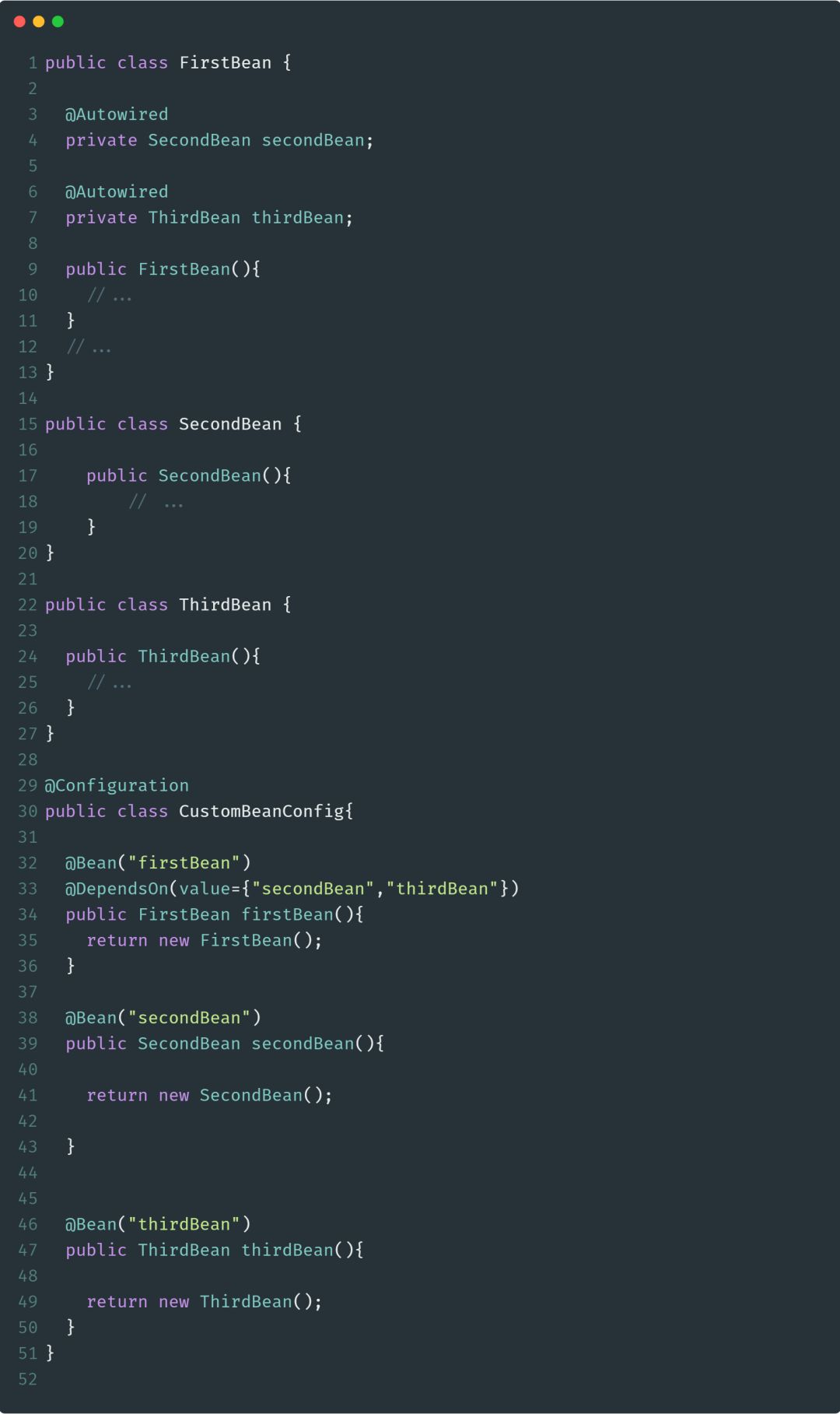
@DependsOn
@DependsOn注解可以配置Spring IoC容器在初始化一个Bean之前,先初始化其他的Bean对象。下面是此注解使用示例代码:
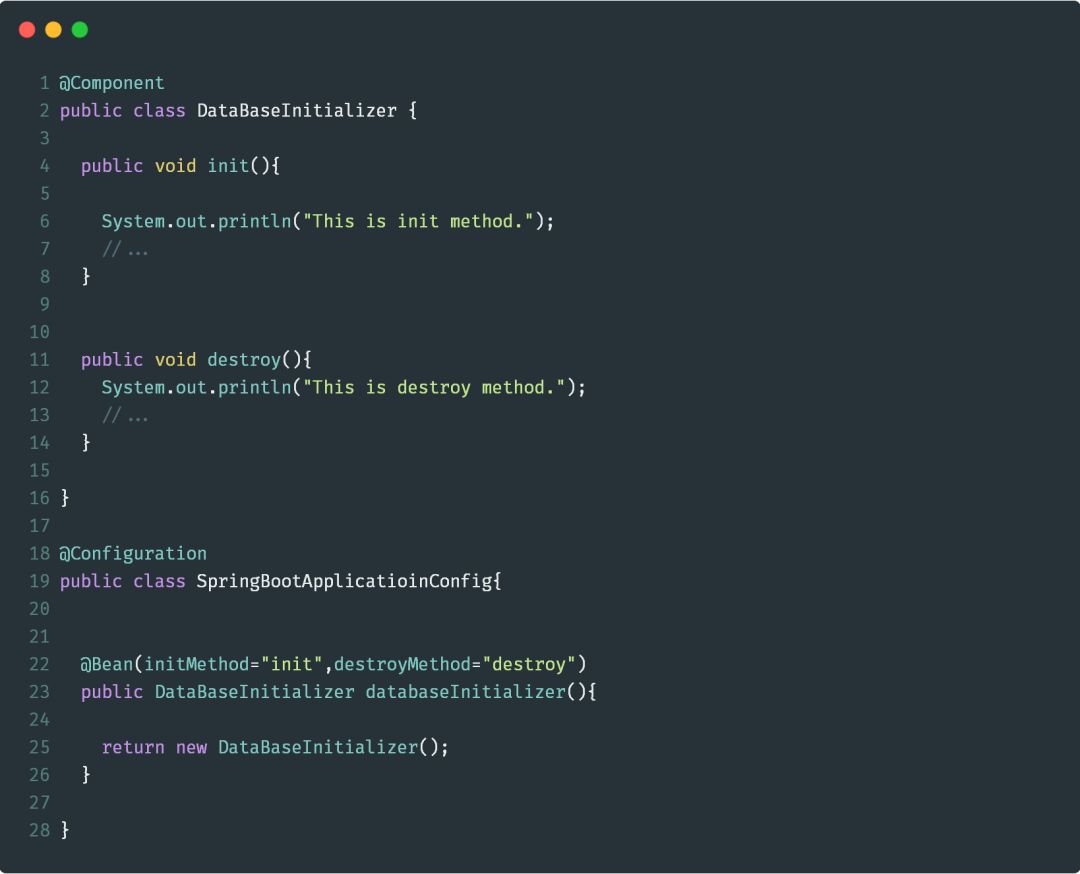
@Bean
@Bean注解主要的作用是告知Spring,被此注解所标注的类将需要纳入到Bean管理工厂中。@Bean注解的用法很简单,在这里,着重介绍@Bean注解中initMethod和destroyMethod的用法。示例如下:
Scops注解
@Scope
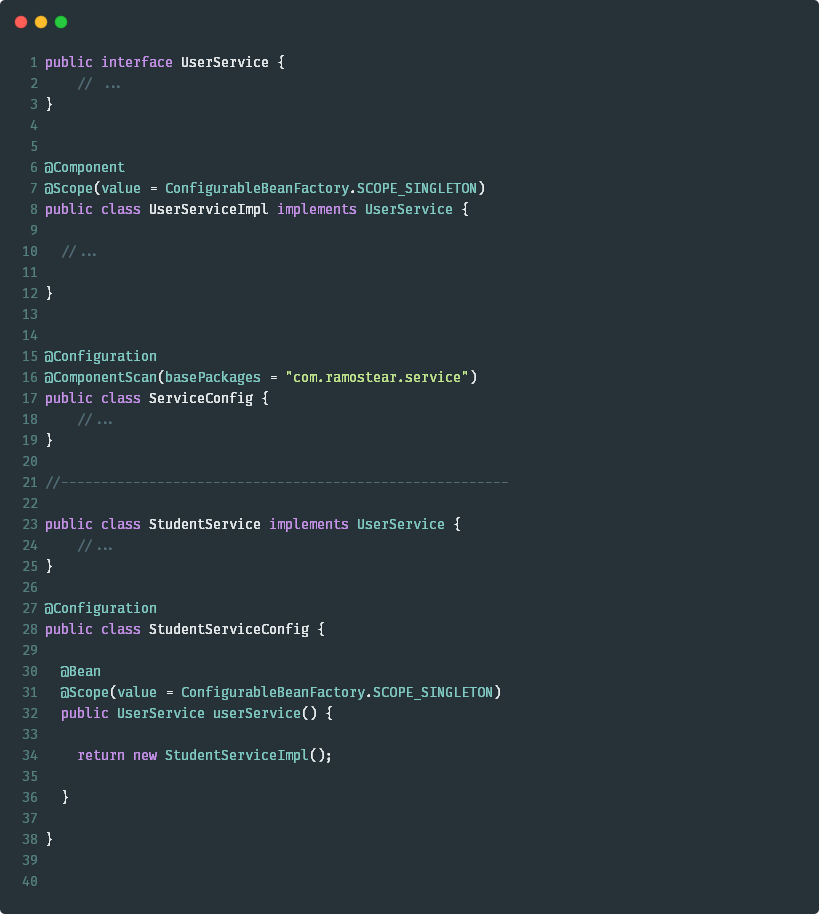
@Scope注解可以用来定义@Component标注的类的作用范围以及@Bean所标记的类的作用范围。@Scope所限定的作用范围有:singleton、prototype、request、session、globalSession或者其他的自定义范围。这里以prototype为例子进行讲解。
当一个Spring Bean被声明为prototype(原型模式)时,在每次需要使用到该类的时候,Spring IoC容器都会初始化一个新的改类的实例。在定义一个Bean时,可以设置Bean的scope属性为prototype:scope=“prototype”,也可以使用@Scope注解设置,如下:
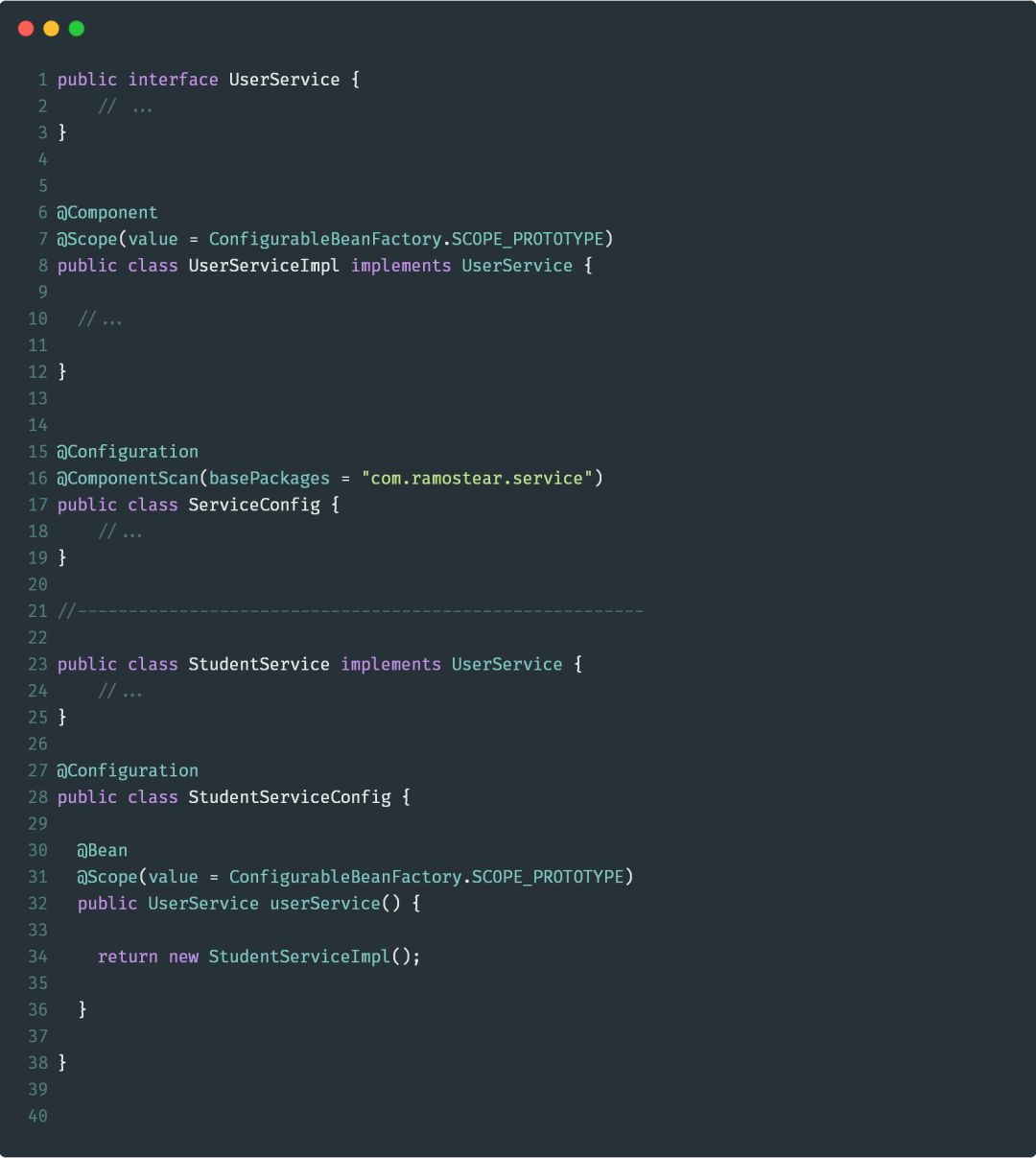
@Scope(value=ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROPTOTYPE)
下面将给出两种不同的方式来使用@Scope注解,示例代码如下:
@Scope 单例模式
当@Scope的作用范围设置成Singleton时,被此注解所标注的类只会被Spring IoC容器初始化一次。在默认情况下,Spring IoC容器所初始化的类实例都为singleton。同样的原理,此情形也有两种配置方式,示例代码如下:
四、容器配置注解
@Autowired
@Autowired注解用于标记Spring将要解析和注入的依赖项。此注解可以作用在构造函数、字段和setter方法上。
作用于构造函数
下面是@Autowired注解标注构造函数的使用示例:

作用于setter方法
下面是@Autowired注解标注setter方法的示例代码:

作用于字段
@Autowired注解标注字段是最简单的,只需要在对应的字段上加入此注解即可,示例代码如下:
@Primary
当系统中需要配置多个具有相同类型的bean时,@Primary可以定义这些Bean的优先级。下面将给出一个实例代码来说明这一特性:

输出结果:
this is send DingDing method message.
@PostConstruct与@PreDestroy
值得注意的是,这两个注解不属于Spring,它们是源于JSR-250中的两个注解,位于common-annotations.jar中。@PostConstruct注解用于标注在Bean被Spring初始化之前需要执行的方法。@PreDestroy注解用于标注Bean被销毁前需要执行的方法。下面是具体的示例代码:

@Qualifier
当系统中存在同一类型的多个Bean时,@Autowired在进行依赖注入的时候就不知道该选择哪一个实现类进行注入。此时,我们可以使用@Qualifier注解来微调,帮助@Autowired选择正确的依赖项。下面是一个关于此注解的代码示例:

五、Spring Boot注解
@SpringBootApplication
@SpringBootApplication注解是一个快捷的配置注解,在被它标注的类中,可以定义一个或多个Bean,并自动触发自动配置Bean和自动扫描组件。此注解相当于@Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration和@ComponentScan的组合。
在Spring Boot应用程序的主类中,就使用了此注解。示例代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application{
public static void main(String [] args){
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration注解用于通知Spring,根据当前类路径下引入的依赖包,自动配置与这些依赖包相关的配置项。
@ConditionalOnClass与@ConditionalOnMissingClass
这两个注解属于类条件注解,它们根据是否存在某个类作为判断依据来决定是否要执行某些配置。下面是一个简单的示例代码:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(DataSource.class)
class MySQLAutoConfiguration {
//...
}
@ConditionalOnBean与@ConditionalOnMissingBean
这两个注解属于对象条件注解,根据是否存在某个对象作为依据来决定是否要执行某些配置方法。示例代码如下:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(name="dataSource")
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory(){
//...
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public MyBean myBean(){
//...
}
@ConditionalOnProperty
@ConditionalOnProperty注解会根据Spring配置文件中的配置项是否满足配置要求,从而决定是否要执行被其标注的方法。示例代码如下:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(name="alipay",havingValue="on")
Alipay alipay(){
return new Alipay();
}
@ConditionalOnResource
此注解用于检测当某个配置文件存在使,则触发被其标注的方法,下面是使用此注解的代码示例:
@ConditionalOnResource(resources = "classpath:website.properties")
Properties addWebsiteProperties(){
//...
}
@ConditionalOnWebApplication与@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication
这两个注解用于判断当前的应用程序是否是Web应用程序。如果当前应用是Web应用程序,则使用Spring WebApplicationContext,并定义其会话的生命周期。下面是一个简单的示例:
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
HealthCheckController healthCheckController(){
//...
}
@ConditionalExpression
此注解可以让我们控制更细粒度的基于表达式的配置条件限制。当表达式满足某个条件或者表达式为真的时候,将会执行被此注解标注的方法。
@Bean
@ConditionalException("${localstore} && ${local == 'true'}")
LocalFileStore store(){
//...
}
@Conditional
@Conditional注解可以控制更为复杂的配置条件。在Spring内置的条件控制注解不满足应用需求的时候,可以使用此注解定义自定义的控制条件,以达到自定义的要求。下面是使用该注解的简单示例:
@Conditioanl(CustomConditioanl.class)
CustomProperties addCustomProperties(){
//...
}
0 条评论